77665544
Inorganic Computation lab molecule report
NH3 analysis
| heading | heading |
|---|---|
| Molecule name | NH3 |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000485 |
| Final energy | -56.55776873 a.u. |
| Point group | C3v |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 |
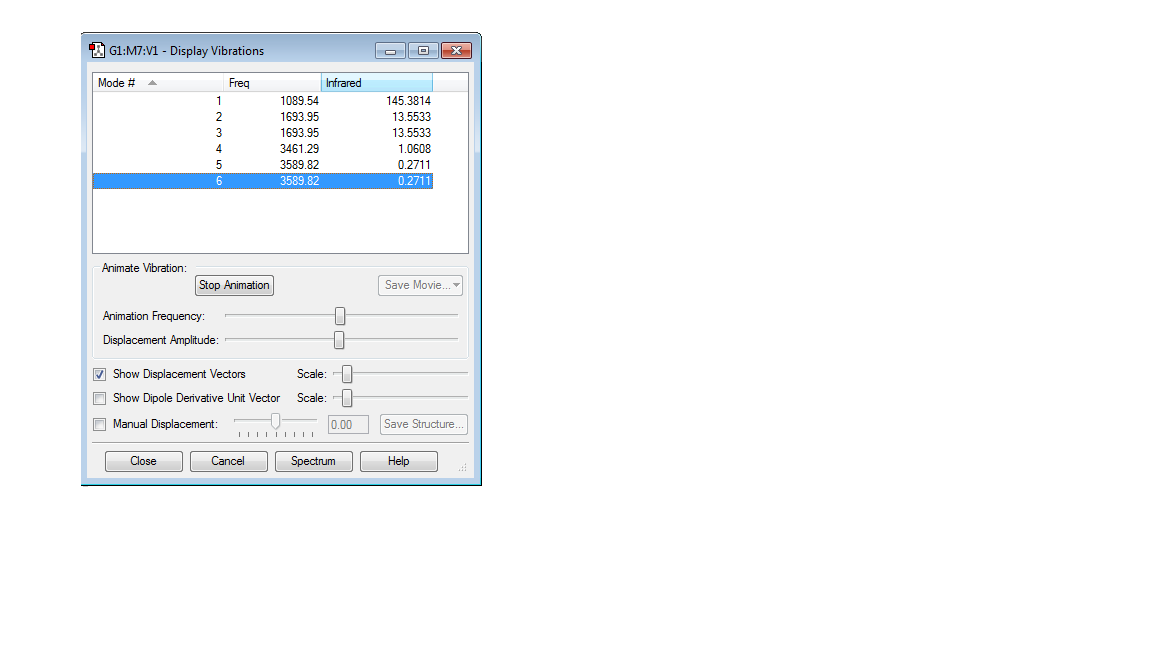
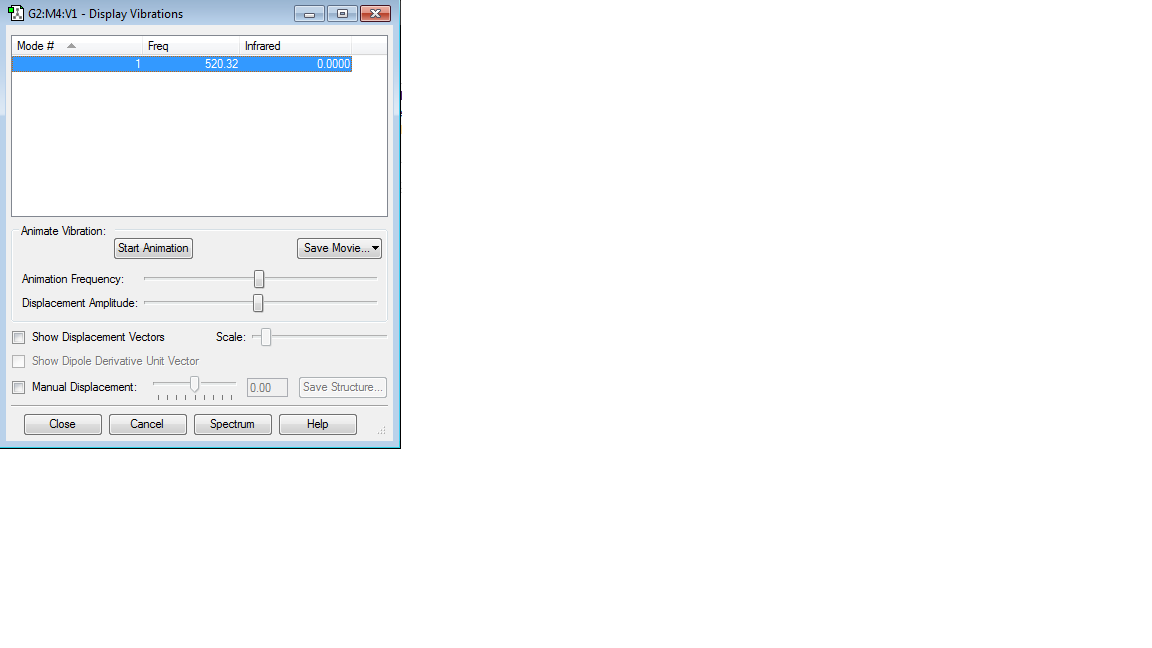
Table showing vibrations
Vibrational questions
1) How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
6
2)Which modes are degenerate?
2&3,5 & 6
3)Which modes are bending vibrations and which modes are bond stretch vibrations?
1,2 & 3 are bending vibrations whereas 4,5 & 6 are bond stretch vibrations
4) 4
5) one mode is known as the umbrella mode, which mode is this?
Mode 1
6) How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia
There are 6 modes but as 4 of them are degenerate, this gives 4 bands as there are 4 distinct frequencies.
Charge distribution for ammonia
The expectation for the charges on the nitrogen atom and the hydrogen atoms is that nitrogen would have the highest charge density, being more negative. This is because nitrogen is a more electronegative atom. The actual charges were that Nitrogen had a charge of: -1.125 and each hydrogen atom had a charge of: +0.375. 0.375*3 is +1.125. This means that overall ammonia is neutral.
N2 and H2 analysis
molecule name: N2
Calculation method: B3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
RMS gradient: 0.00000060
Final energy: -109.52412868 a.u.
Point group: D∞h
| heading | heading |
|---|---|
| Molecule name | N2 |
| Calculation method | B3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy | -109.52412868 a.u. |
| Point group | D∞h |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
test molecule |
| heading | heading |
|---|---|
| Molecule name | H2 |
| Calculation method | B3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000017 |
| Final energy | -1.17853936 a.u. |
| Point group | D∞h |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
test molecule |
Energy calculations
In order to calculate the energy of the reaction, the following calculation can be used, using the stoichiometry from the overall equation.
E(NH3)= -56.55776873
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375
E(N2)= -109.52412868
E(H2)= -1.17853936
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05579074
All in atomic units.
In order to convert this answer from a.u. to kJ mol-1 this value can be multiplied by 2625.5.
This gives a value of -146.48 kJ mol-1.
As energy is released when this reaction takes place, this means that NH3 has a lower energy than the two gaseous reactants, meaning that it is more stable.
BH3 analysis
| heading | heading |
|---|---|
| Molecule name | BH3 |
| Calculation method | B3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| RMS gradient | 0.00305259 |
| Final energy | -26.61511243 a.u. |
| Point group | D3h |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000017 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000011 0.001200 YES
test molecule |
Charges
The charges present on the hydrogen are -0.099 a.u. with 3 hydrogens present. This means that the charge on boron is +0.297. This means that hydrogen is more electronegative than boron.
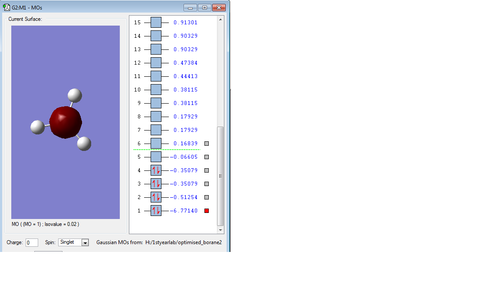
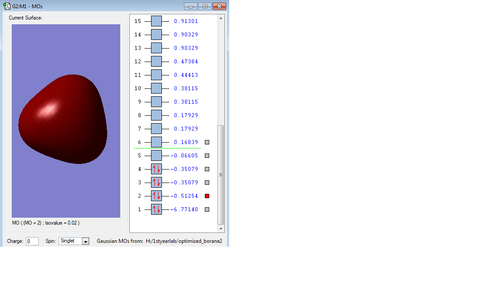
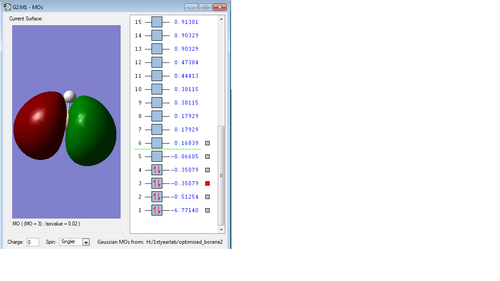
Molecular orbitals of Borane
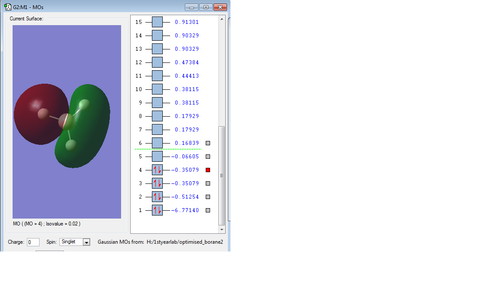
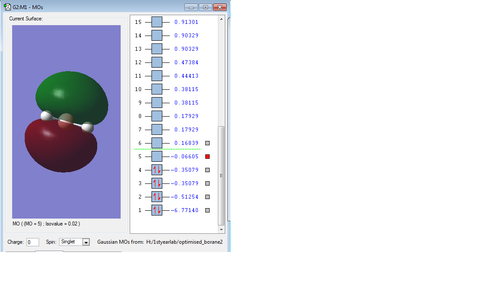
Cl2 analysis
| heading | heading |
|---|---|
| Molecule name | Cl2 |
| Calculation method | B3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| RMS gradient | 0.00002511 |
| Final energy | -920.34987886 |
| Point group | D∞h |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES