01365309CYY
NH3 molecule
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NH3 molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to here
| Molecule name | NH3 |
|---|---|
| N-H bond length | 1.01798 Å |
| H-N-H bond angle | 105.741° |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy E(RB3LYP) | -56.55776873 (au) |
| Point Group | C3V |
bbh3_opt
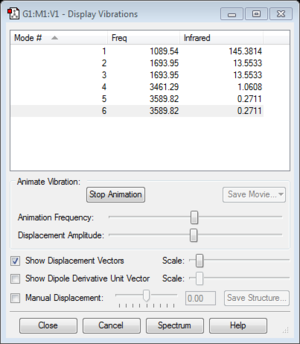
- how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? 3*4-6=6
- which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? Mode 2 and 3 are degenerate because they have same frequency. Frequency is directly proportional to frequency. Mode 5 and 6 are also degenerate with same frequency.
- which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? 1,2,3 bending; 4,5,6 stretch
- which mode is highly symmetric? 4
- one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? 1
- how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?2. Mode 4,5 and 6 are too small to see a band in the spectrum. Mode 2 and 3 are degenerate. Thus there are only two bands for 1 and 2&3.
| Charge on N atom | -1.125 |
|---|---|
| Charge on H atom | +0.375 |
The charge on N atom is expected to be negative because N is more electronegative than H atom. Thus, N is partially negative and H atoms are partially positive. 3 H atoms totally carry +1.125 charge which balances charge on N (-1.125), giving an overall neutral NH3 molecule.
N2
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
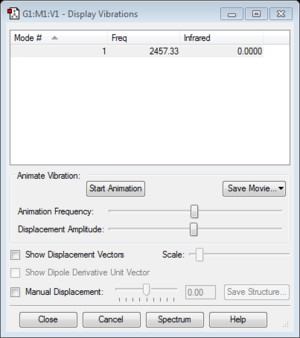
N2 molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to here
| Molecule name | N2 |
|---|---|
| bond length | 1.092 Å |
| bond angle | 180° |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy E(RB3LYP) | -109.52412868 (au) |
| Point Group | D∞h |
| frequency | 2457.33 |
H2
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
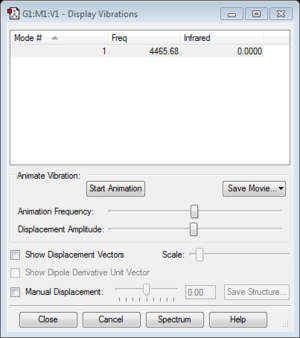
H2 molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to here
| Molecule name | H2 |
|---|---|
| H-H bond length | 0.74279 Å |
| H-H bond angle | 180° |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy E(RB3LYP) | -1.17853936 (au) |
| Point Group | D∞h |
| frequency | 4465.68 |
The Haber-Bosch process:N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
This is the commercial process used to synthesis ammonia from hydrogen and nitrogen with catalyst iron in industrial use. Ammonia is commonly used as a fertiliser. A problem firstly came for the reaction was that N2 is a very stable molecule as this method was discovered. Many attempts had tried for less stable molecules but failed because of thermodynamic or entropy problem. Thus, a catalyst was introduced together with high temperature and high pressure to shift the equilibrium to the ammonia side and increase the rate of reaction.
- E(NH3)= -56.55776873 (au)
- 2*E(NH3)= (-56.55776873)*2=-113.1155375 (au)
- E(N2)= -109.52412868 (au)
- E(H2)= -1.17853936 (au)
- 3*E(H2)= (-1.17853936)*3=-3.53561808 (au)
- ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= (-113.1155375)-(-109.52412868-3.53561808)=-0.05579074 (au) = -146.48 kJ/mol
The energy change is negative so energy decreases when converting hydrogen and nitrogen gas to ammonia. Thus, ammonia has lower energy which is more stable.
project molecule CF4
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000078 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000042 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000133 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000071 0.001200 YES
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.3294 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.3294 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.3294 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R4 R(1,5) 1.3294 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(2,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(3,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(4,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(2,1,5,3) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(2,1,5,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(3,1,5,4) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CF4 molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to here
| Molecule name | CF4 |
|---|---|
| C-F bond length | 1.32939 Å |
| C-F bond angle | 109.471° |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy E(RB3LYP) | -437.47627267 (au) |
| Point Group | Td |
| Charge on C atom | +1.401 |
|---|---|
| Charge on F atom | -0.350 |
The charge on F atom is expected to be negative because F is more electronegative than C atom. Thus, F is partially negative and C atoms are partially positive. 4 F atoms carry -1.400 charge which balances charge on C (+1.401), giving an overall neutral CF4 molecule.
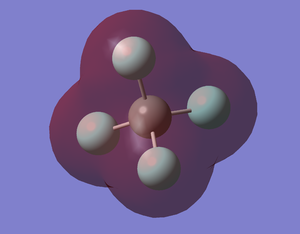
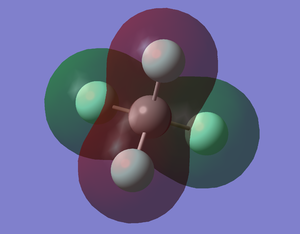
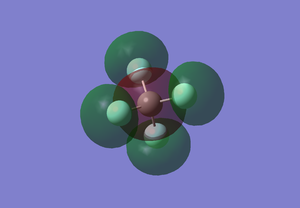
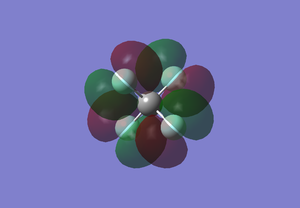
CF4 MO5
This shows the 1s of C only. The enegy level is -10.52436 au. This MO is occupied. F is more electronegative than C so the 1s orbital of F has lower energy. As the 1s orbitals of C and F are futher apart so they do not overlap to form bonding orbital. Thus, this is the non-bonding orbital of C1s.
CF4 MO6
This shows the bonding orbital of 4 F2s and C2s. This MO is occupied. The energy level is -1.36790 au, which is much higher in energy than the 1s orbital of C.
CF4 MO8
This shows the bonding orbital of F2s and C2p. This MO is occupied. Two of F2s overlap with the upper part of C2p and the other two overlap with the bottom part of C2p. As C2p has opposite phase of upper and bottom part, the bonding orbital shows the opposite phase. The energy level is -1.25478 au, which is slightly higher in energy.
CF4 MO10
This is the antibonding orbital of 4 F2s and C2s. This MO is occupied. The energy level is -0.725760 au. The C2s has opposite phase with 4F2s orbital. This has higher energy than the bonding orbital.
CF4 HOMO
This is the HOMO which is the highest occupied molecular orbital. The energy level is -0.42856 au which is high in energy. It is a non-bonding orbital since only F2p overlap oppsitely with each other.
HCl molecule
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000090 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000090 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000139 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000197 0.001200 YES
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.286 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
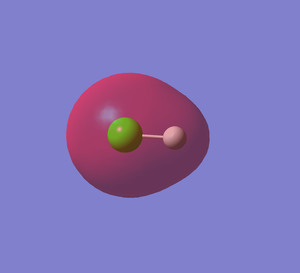
HCl molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to here
| molecule name | HCl |
|---|---|
| H-Cl bond length | 1.28599 Å |
| H-Cl bond angle | 180° |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy E(RB3LYP) | -460.80077875 (au) |
| Point Group | C∞v |
| charge on H atom | +0.284 |
|---|---|
| charge on Cl atom | -0.284 |
The charge on Cl atom is expected to be negative because Cl is more electronegative than H atom. Thus, Cl is partially negative and H atoms are partially positive. Cl atoms carry -0.284 charge which balances charge on C (+0.284), giving an overall neutral HCl molecule.

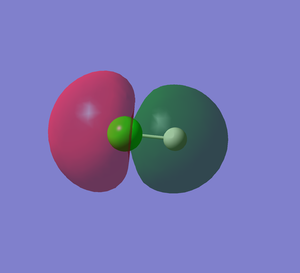
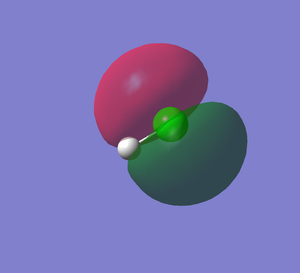
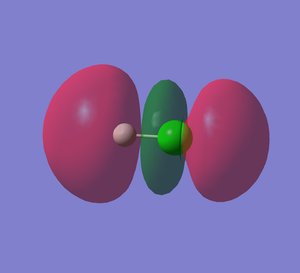
HCl MO5
This shows the non-bonding orbital of Cl 2p orbital. This MO is occupied. The energy level is -7.22836 au, which is much higher in energy than the 1s orbital of H so they do not overlap.
HCl MO6
This shows the bonding orbital of Cl 3s and H1s. This MO is occupied. The energy level is -0.84773 au, which is much higher in energy than the non-bonding orbital of Cl 2p orbital.
HCl MO7
This shows the bonding orbital of H1S and Cl 2p. This MO is occupied. The energy level is -0.47433 au, which is higher in energy than the bonding orbital of Cl 2s 3 and H1s.
HCl MO8
This is the non-bonding orbital of Cl 2p orbital. Since there three dimensions of p orbital , only one dimension(z) can overlap with H 1s. The rest two would form non-bonding orbital.This MO is occupied. The energy level is -0.33163 au.
HCl MO 10
This is the LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital). This is the anti-bonding orbital of Cl 2p and H1s. The energy level is 0.01366 au.
