It:Bradykinin.2nd
Description
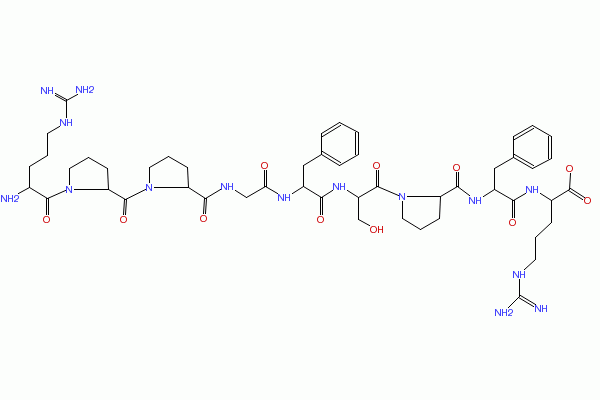
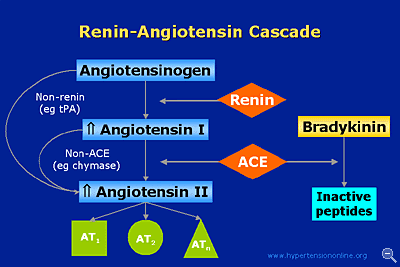
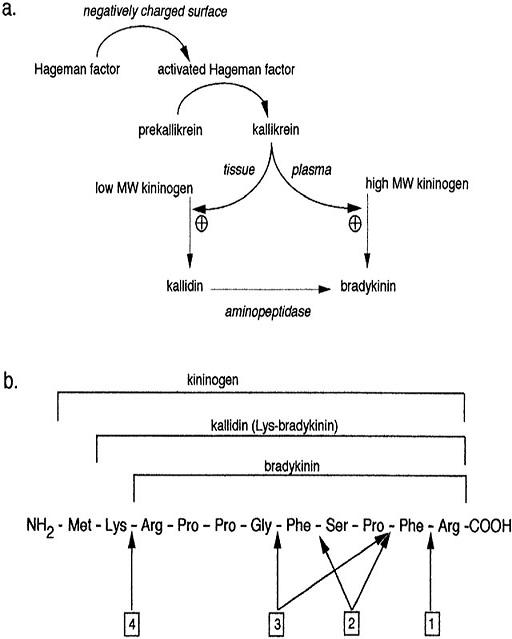
Bradykinin is an activates pain receptors. Bradykinin induces smooth muscle contraction; activates Ca2+-dependent nitric oxide synthetase. Bradykinin can also increase capillary permeability. Bradykinin is a potent stimulator of nitric oxide formation by vascular endothelium. Bradykinin also stimulates prostacyclin formation. Bradykinin (BK), a nanopeptide (Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg), is the prototype of a family of powerful vasodilatory peptides, the kinins. Although known for a long time only as a pro-inflammatory peptide, BK is now considered an important mediator of the benefits of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi). BK is also an important mediator of a new class of drugs, vasopeptidase inhibitors.
History
Bradykinin was discovered by three Brazilian physiologists in 1948 its powerful hypotensive effects in animal preparations. Bradykinin was detected in the blood plasma of animals after the addition of venom of Bothrops jararaca (Brazilian lancehead snake), which was brought by Rosenfeld from the Butantan Institute. This discovery was part of a continuing study on circulatory shock and proteolytic enzymes related to the toxicology of snake bites, started by Rocha e Silva as early as 1939. Bradykinin was to prove a new autopharmacological principle,a substance that is released in the body by a metabolic modification from precursors, which are pharmacologically active."The discovery of bradykinin has led to a new understanding of many physiological and pathological phenomena including circulatory shock induced by venoms and toxins."
2D structure of bradykinin
3D Image of Bradykinin
Snake-like view of Bradykinin
Physiological role
Bradykinin is a potent endothelium-dependent vasodilator, causes contraction of non-vascular smooth muscle, increases vascular permeability and also is involved in the mechanism of pain. In some aspects, it has similar actions to that of histamine, and like histamine is released from venules rather than arterioles.
Bradykinin raises internal calcium levels in neocortical astrocytes causing them to release glutamate.
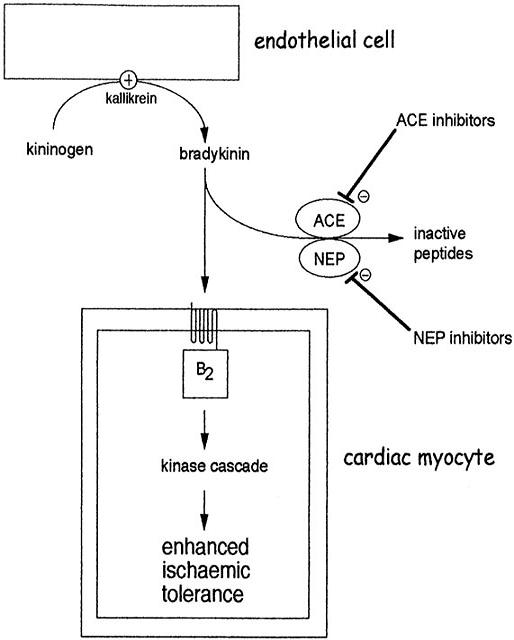
Bradykinin is also thought to be the cause of the dry cough in some patients on angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor drugs. This refractory cough is a common cause for stopping ACE-inhibitor therapy.
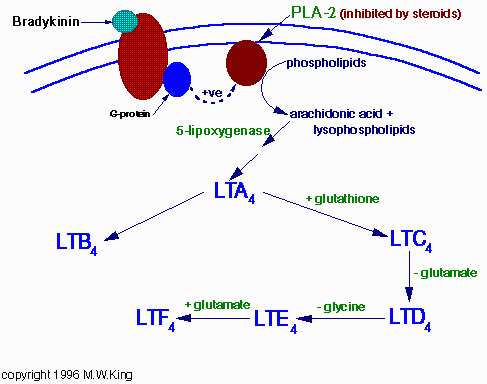
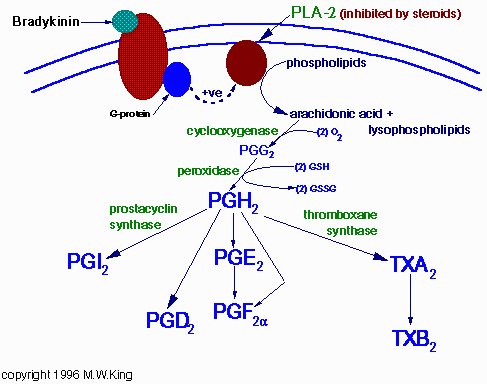
Reaction Mechanism
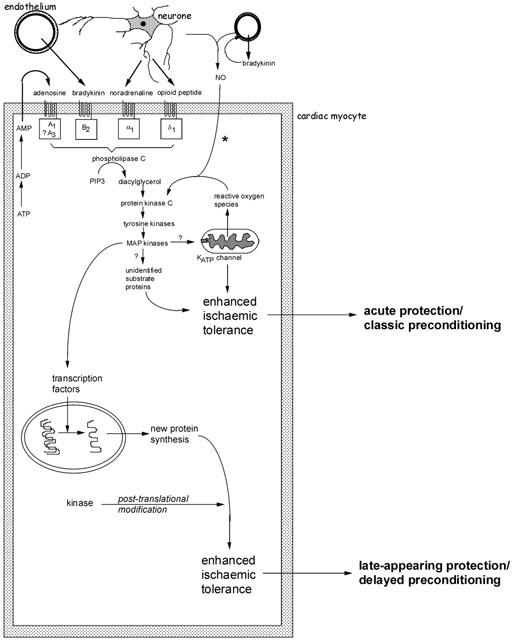
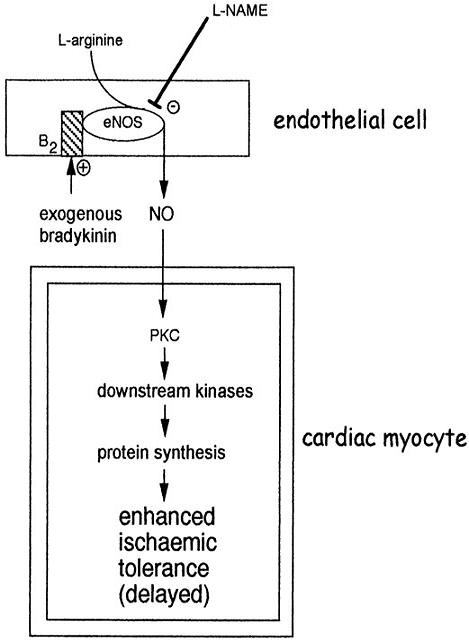
Role of bradykinin in preconditioning and protection of the ischaemic myocardium
Further Reading
- [History and a review of the kinin system
http://www.jstor.org/view/00804649/ap000191/00a00110/0]
- [Bradykinin attenuates glucagon-inducedleucine oxidation in humans
http://ajpendo.physiology.org/cgi/reprint/259/2/E239.pdf]
External Links
- [Use of peptidic bradykinin antagonists for the treatment and prevention of Alzheimer's disease
http://www.patentstorm.us/patents/6245736-description.html]
- [Role of bradykinin in preconditioning and protection of the ischaemic myocardium
- [Mechanisms of ACE Inhibitor Angioedema
http://www.clinimmsoc.org/meetings/summerschool06/presentations/banerji_aleena.pdf]